
Maybe someday in the future, we will spend this time...
Smart alarm clock: Wake up, project time on the ceiling, remotely open curtains and TV
Smart TV: touch screen TV, free internet access to weather conditions and real-time traffic conditions
Smart refrigerator: Through the mobile phone or computer, you can know the quantity of food in the refrigerator and the information of freshness and shelf life anytime and anywhere. It can provide users with healthy recipes and nutrition taboos and can remind users to regularly supplement foods.
Smart cars: Auto driving. There is a set of navigation information database, GPS positioning system, road condition information system, vehicle anti-collision system, emergency alarm system and autopilot system.
Smart computers: intelligent multi-tasking, smart acceleration, and smart energy saving.
Smartphone: It refers to a generic name of a mobile phone that has a separate operating system like a personal computer and can achieve wireless network access through a mobile communication network.
This is the scene of life presented to us by smart cities. What is a smart city?
The so-called smart city is based on Internet of Things, cloud computing and other next-generation information technology and a variety of social networking, shopping networks, Internet finance and other integrated tools and methods of integrated applications, including smart grid, smart buildings, intelligent security systems, intelligent water treatment System, intelligent transportation, etc.
Smart cities can more effectively implement city grid management and services. For example, there are more than 2 million parts facilities and more than 8 million people in Wuhan, and there are more than 600,000 incidents each year. We can intelligently collect data and intelligently analyze and effectively manage and service these parts and facilities, population, and events.
Intelligent transportation systems, through the transformation of traditional transportation systems, improve the information, intelligence, integration, and networking of transportation systems, intelligently collect traffic information, traffic, noise, roads, traffic accidents, weather, temperature, etc., thereby protecting people, The mutual exchanges between cars, roads and the environment will improve the efficiency, mobility, safety, accessibility, and economy of the transportation system, and will help protect the environment and reduce energy consumption.
At present, it is generally believed that sensors are the key to the construction of smart cities.
Songdo, South Korea
South Korea has always been at the forefront of the application of new technology countries. The country boasts the world’s fastest consumer Internet, and its culture also recognizes the application of new technologies. Therefore, it is not surprising that South Korea has become one of the first countries to try to build a smart city by exploiting the potential of the Internet. In 2001, South Korea took the lead in establishing a high-tech city where people can live in the future through the reclamation of the sea: Songdo (Songdo). In Songdo, power facilities that are fully connected to the network will not only provide city managers with information on current electricity usage, but they will also help local residents control their electricity usage. Traffic information sensors have also been pre-positioned on public roads in Songdo so as to provide the city's traffic departments with specific information on traffic conditions and allow traffic managers to intelligently reset traffic lights to reduce the incidence of traffic jams and traffic accidents. At the same time, it can optimize the distribution of traffic and people flow. These "smart roads" are connected to the central control room through the network and can play an early warning role before the earthquake.
Santander, Spain
Santander, Spain is a medium-sized town. In order to reduce air and noise pollution, Santander has begun to seek the help of technology and become one of the pilot cities for large-scale sensor deployment. By launching the "Smart Santander" project, the city has already deployed about 10,000 electronic surveillance equipment. Each device includes two radio transceivers to communicate with other devices, GPS and sensors, and to monitor urban CO2 emissions, noise, temperature, ambient light, and even parking spaces in a particular area. Each monitoring device communicates information in real time over the Internet so that drivers can find the next suitable parking lot via mobile applications or smart signals.
American city group
In the United States, several municipalities have begun installing new sensors in the city's sewers and waterway systems, which has saved them a lot of money. For example, in South Bend, Indiana, a monitoring sensor device provided by IBM is installed, which can aggregate data collected from different government departments and then convert this data into useful information. This reduced the incidence of sewer overflow incidents in South Bend City by 23% and completely eliminated the sewer blockage. South Bend City expects to be able to recover the cost of installing new technology equipment in less than two years. In Miami-Dade County, Florida, municipalities said using smart sensors can help them repair tap water accidents faster. They expect that this will save $1 million in annual funding and reduce water consumption by 20%.
Under the current wave of global smart city construction, it seems that only by arranging enough data acquisition devices in the city, that is, more sensors, can we meet the needs of smart city construction. However, at the “2014 Global Smart City Summit†sponsored by the China Urban Science Research Center Digital City Engineering Research Center, the participating experts expressed such views. “Building a smart city is not putting more sensors and collecting more data. It is Break down the island of information and reintegrate the information resources.†Before the appearance of the Internet of Things, various parts of the city, such as medical information, traffic information, environmental protection information, and housing information, were isolated from each other and were chimney-like. Form sharing. “The arrival of the Internet of Things era has made it possible to build a smart city.†Oracle experts said that to build a smart city, it is necessary to reintegrate the information of various parts of the city and share relevant information.
From this perspective, building a smart city must first break the “information islandâ€, realize the sharing of information and data, and manage it in a unified manner so that the data can truly serve the managers. Particular emphasis should be placed on breaking the industry's fragmented, closed information architecture and highlighting the overall effectiveness of informationization. "Does not break the interests of the department, even if put more sensors, still can not solve the problem of information sharing." Some experts put forward. Taking the San Francisco Smart Parking System in the United States as an example, the government will re-allocate parking spaces by sharing information on all parking spaces in the city, implement flexible charging, and make the city's parking spaces into APP software, allowing citizens to download mobile phones. For the driver, download this software, you can find parking spaces in various locations nearby and understand the charge information. At the same time, building a smart city should start with top-level design. The top-level design of smart cities is aimed at the construction of smart cities. From an overall perspective, the overall architecture is designed to coordinate all aspects of the entire architecture, all levels, various participation forces, various positive factors and negative constraints. Consider and design. The top-level design of a smart city includes the institutional mechanism architecture, business architecture, performance architecture, information architecture, and technology architecture.
Internet of Things related technologies have been widely used in transportation, logistics, industry, agriculture, medical, health, security, home, tourism, military and other more than 20 areas, in the next 3 years China's Internet of Things industry will be in the smart grid, smart home, The digital city, smart medical care, automotive sensors and other fields are the first to be popularized and it is expected to achieve a total output value of about RMB 3 trillion.
Carbon fiber 3D Printer Filament 35 types 45 colors 1.75mm 2.85mm 3mm abs pla filament
Product introduce:
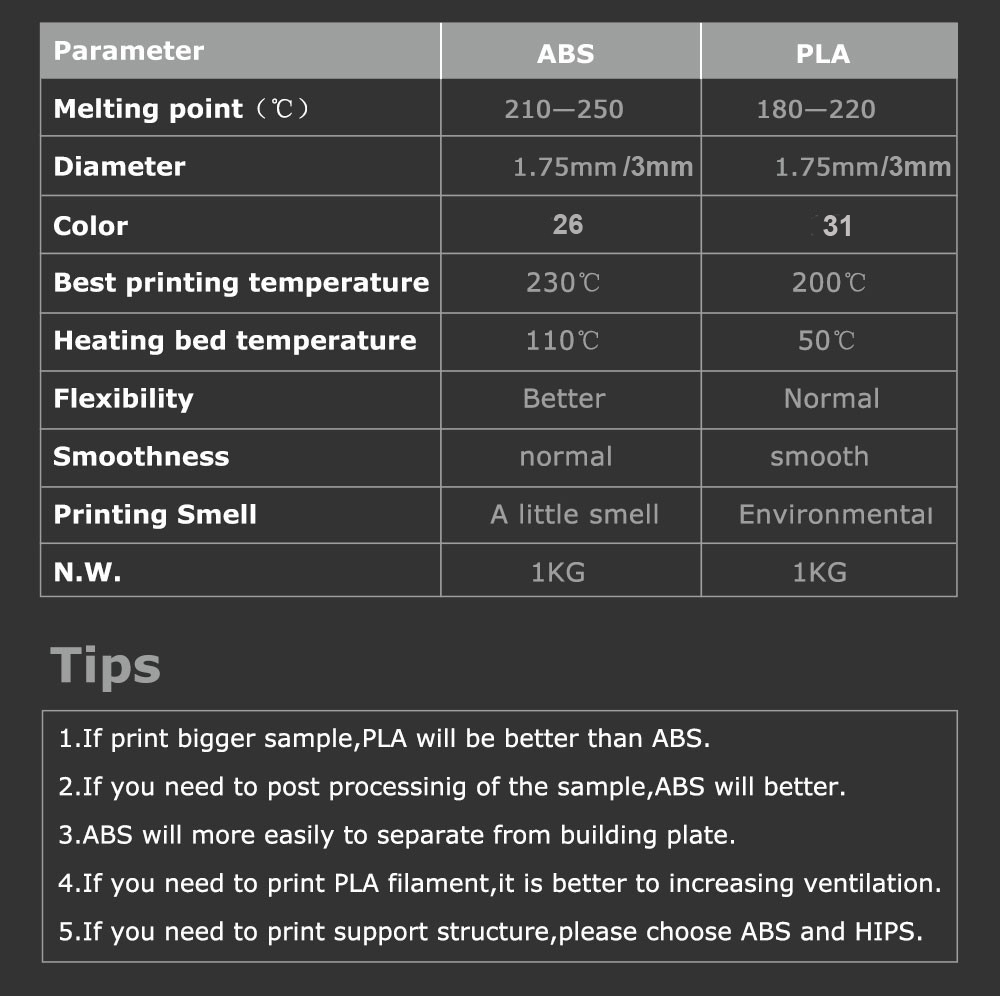
PLA filament:
Carbon fiber 3d printer filament, this is the best filament on the market.The 1.75mm filament holds a diameter tolerance of 0.02mm/0.0008" which improves reliability and quality of output and comes vacuum-sealed with the desiccant on a 1kg (2.2lb) reel.
3D Printer Filament Materials PLA allows higher print speed, more accurate placement of material with proper cooling (it does not shrink as much) and also thinner build heights because of less resistance from the plastic coming out the nozzle.
Compatible 3D Printers:
3D Printer Consumables suitable for Makerbot,RepRap, UP, Flashforge, Leapfrog, Ultimaker,Printrbot and any other FDM 3D printer!
Color what we have for ABS & PLA filament
Basic color: White,Black,Red,Blue,Yellow,Green,Nature,
Other color: Silver,Grey,Gold,Pink,Purple,Orange,Yellow gold,Wood,Chrismas green,Galaxy blue,Transparent
Fluorescent series: Flurescent Red, Flurescent Yellow, Flurescent Green, Flurescent Blue
Luminous series: Luminous Green, Luminous Blue
Color changing series : Blue green to yellow green, Blue to white,Purple to Pink,Grey to White
Accept customer PMS color
KEYUACE 3D Printer Filament Catalog And Parameter
Material: PLA ABS ABS-CE HIPS PP Nylon PETG Wood Flexible Rubber PVA
Color: 31 26 26 15 25 4 5 1 8 1
Printing Temp: 190-220 200-240 210-240 190-230 210-260 210-240 230-260 200-230 200-230 190-240
Net Weight: 1KG 0.8KG 0.5KG 0.5KG, 0.25KG
Spool size out diameter: 180mm+ inner diameter 57mm + Reel diameter 95mm
Diameter: 1.75mm and 3mm
Tolerlance roundness: +/- 0.02-0.04mm
Compatible with Makerbot,UP,Afinia,Leapfrog Creatr,Builder,Reprap,Ultimaker and any other FDM 3D Printers
Similar Makerbot Makerbot / Makerbot / / Taulman Laywood Makerbot /
Certification Rohs,SGS,MSDS
Application Education; Engineering; Entertainment;Orthopedics etc.
Shipping information:
Shipping Weight: 1.35KG
Spool Diameter: 180mm
Net Weight: 2.2lbs/1kg
Spool Width: 72mm
Box size: 190x190x85mm
Hub Hole Diameter: 38mm l 60mm
Carton pack:12 spools
Carton Size: 290x390x390mm
Quality control:
a) All of our 3D printer filaments are 100% virgin material,never use recycled material or regrind material,and all had achieved the latest certificate.
b) Before the mass production,our engineer always do the test to make sure that each batch of new raw materials must be printed by 3D printer.
c) The Laser diameter runs automatically to control the diameter of the filaments and keeps it in a right range of 1.75/3.0mm,and our engineer will adjust it immediately when it alarms to indicate of wrong size,and this unqualified filament will be cut off and never use it.
d) To keep the filaments dry,each roll of filament is packed in a vacuumed polybag with a desiccant inside of it.
Product images:
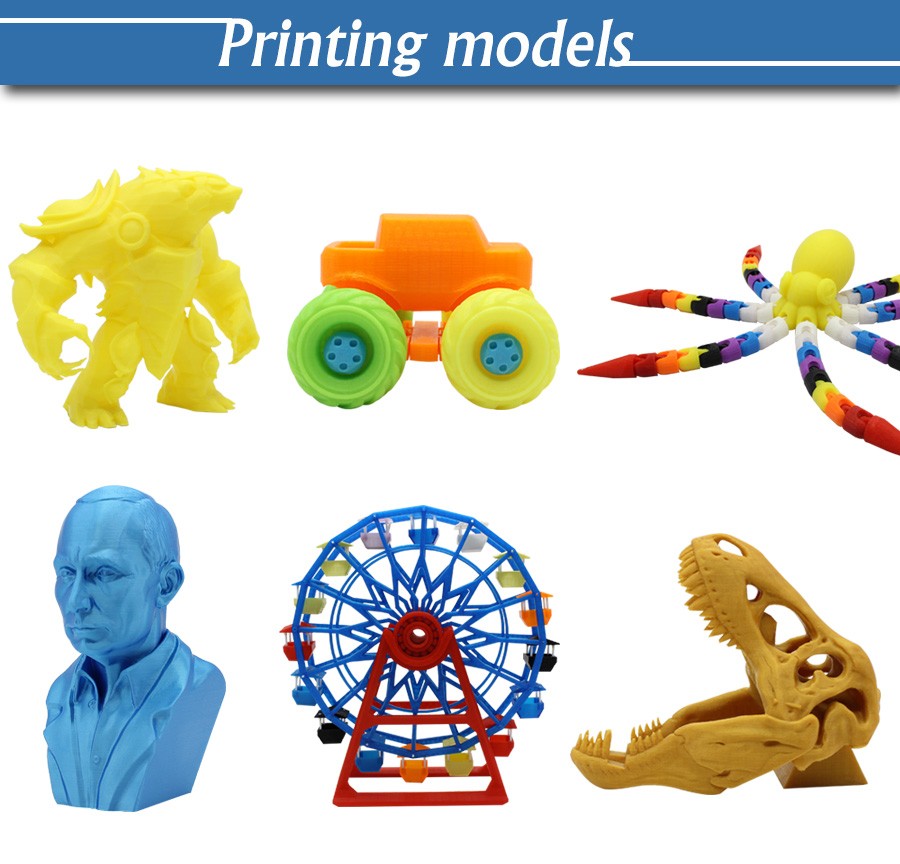



3D Printer Filament
3D Printer Consumables,High Temperature 3D Filament,3D Printer Filament Materials
KEYUACE Materials Co., Ltd. , http://www.insulationtubing.com
