Introduction to the structure and basic principle of cylinders, SMC China Ltd.
The cylinder plays a decisive role in the assembly line. How much do you know about the cylinder? The following briefly describes the structure and basic principle of the cylinder:
One, cylinder - cylinder type
Pneumatic actuators that convert the pressure energy of compressed gas into mechanical energy. The cylinder has two types of reciprocating linear motion and oscillating motion (see figure). The reciprocating linear motion cylinder can be divided into single acting, double acting, diaphragm type and impact cylinder. 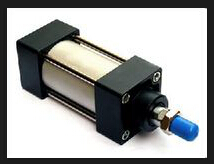
1 single-acting cylinder: only one end has a piston rod, from the side of the piston to generate energy to generate air pressure, air pressure to push the piston to produce thrust out, return by spring or self-weight.
2 Double-acting cylinders: alternating air supply from both sides of the piston, output force in one or two directions.
3 Diaphragm cylinder: The piston is replaced by a diaphragm and the force is only output in one direction and is reset by a spring. Its sealing performance is good, but the stroke is short.
4 Impact Cylinder: This is a new type of component. It converts the pressure energy of the compressed gas into the kinetic energy of the piston's high-speed (10-20m/s) motion for work. The impact cylinder adds a middle cover with a spout and a vent. The middle cover and the piston divide the cylinder into a three-chamber of a gas storage chamber, a head chamber, and a tail chamber. It is widely used in various operations such as blanking, punching, crushing and molding. The oscillating cylinder is called a swing cylinder, in which the inner space is divided into two by a vane, and the two chambers are alternately supplied with gas. The output shaft is oscillating and the swing angle is less than 280°. In addition, there are rotary cylinders, gas-liquid damping cylinders, and stepping cylinders.
Second, the role of the cylinder:
The pressure energy of compressed air is converted into mechanical energy, and the drive mechanism makes linear reciprocating, swinging and rotating motions.
Third, the classification of cylinders:
Linear motion reciprocating cylinder, oscillating motion oscillating cylinder, gripper, etc.
Fourth, the structure of the cylinder:
The cylinder is composed of cylinder, end cap, piston, piston rod and seal. Its internal structure is shown in the figure:
Introduction to the structure and basic principle of cylinders, SMC China Ltd.

Five, SMC cylinder principle diagram 1) cylinder
The cylinder bore size represents the output force of the cylinder. The piston should make a smooth reciprocating sliding in the cylinder, and the surface roughness of the inner surface of the cylinder should reach Ra0.8um. For steel tube cylinders, the inner surface should also be plated with hard chrome to reduce frictional resistance and wear, and to prevent corrosion. In addition to the use of high-carbon steel pipe cylinder material, or high-strength aluminum alloy and brass. Small cylinders use stainless steel tubes. For cylinders with magnetic switches or cylinders used in corrosion-resistant environments, cylinders should be made of stainless steel, aluminum alloy, or brass.
The SMC CM2 cylinder piston uses a combination of seals to achieve two-way sealing. The piston and the piston rod are riveted together without nuts.
2) End cap
The end cap is provided with an intake and exhaust vent, and some also have a buffer mechanism in the end cap. A seal ring and a dust ring are provided on the rod end cover to prevent air leakage from the piston rod and prevent external dust from entering the cylinder. A guide sleeve is provided on the side end cover of the rod to improve the guide accuracy of the cylinder, to withstand a small amount of lateral load on the piston rod, to reduce the amount of downward deflection when the piston rod is extended, and to prolong the service life of the cylinder. The guide sleeve usually uses sintered oil-containing alloys and forward-bent copper castings. The end caps used to be malleable cast iron in the past. Nowadays, in order to reduce the weight and prevent rust, aluminum alloy die-casting is often used. The micro-cylinder is made of brass material.
3) Pistons
The piston is a pressured part in the cylinder. In order to prevent the two chambers of the piston from purging each other, piston seals are provided. The wear ring on the piston can improve the guiding performance of the cylinder, reduce wear of the piston seal ring and reduce frictional resistance. The wear ring is made of polyurethane, PTFE, and cloth synthetic resin. The width of the piston is determined by the seal size and the necessary length of the sliding part. The sliding part is too short and can easily cause premature wear and seizure. The material of the piston is usually made of aluminum alloy and cast iron. The piston of the small cylinder is made of brass.
4) Piston rod
The piston rod is the most important part in the cylinder. High-carbon steel is usually used, the surface is plated with hard chrome, or stainless steel is used to prevent corrosion and improve the wear resistance of the seal ring.
5) sealing ring
Parts of a rotary or reciprocating seal are called dynamic seals. The seal of a stationary part is called a static seal.
There are mainly the following methods for connecting the cylinder tube and the end cap:
Integral type, riveted type, threaded connection type, flange type, tie rod type.
6) When the cylinder is working, the piston is lubricated by the oil mist in the compressed air. There are also a small number of lubrication-free cylinders.
Six, cylinder - working principle
Determine the thrust and tension on the piston rod based on the amount of force required for the job. Therefore, when selecting the cylinder, the output force of the cylinder should be slightly margined. If the bore size is selected small, the output force is not enough, and the cylinder can not work normally. However, if the bore diameter is too large, not only the equipment is heavy and the cost is high, but also the air consumption is increased, resulting in energy waste. In the fixture design, force-increasing mechanisms should be used as much as possible to reduce the size of the cylinder.
Introduction to the structure and basic principle of cylinders, SMC China Ltd.
VII. Treatment methods The causes of deformation and leakage of the cylinder joint surface are different, and the occurrence of the deformation of the joint and the deformation is not the same. First, use a long flat ruler and a feeler gauge to check the deformation of the cylinder joint surface. The cause of the leak and the degree of deformation take corresponding maintenance measures. The specific method is as follows:
1. If the deformation of the cylinder is large or if the steam leakage is serious, use the method of grinding and scraping the joint surface. If the deformation of the upper cylinder joint surface is within 0.05mm, the upper cylinder joint surface is used as the reference surface, and red or embossed blue paper is applied to the lower cylinder joint surface. According to traces, scratch the lower cylinder. If the deformation of the upper face of the cylinder is large, apply red dan on the upper cylinder, and use a large flat rule to remove the marks and flatten the upper cylinder. Or take the mechanical processing method to level the upper cylinder joint surface, and then use the upper cylinder as a reference to scrape the lower cylinder joint surface. There are two general methods for scraping the cylinder joint surface:
(1) Bolts that are not tightly coupled to the surface are used to slightly move the upper cylinder forward and backward with the jack, and the scraping is performed according to the coloring of the red cylinder of the lower cylinder. This method is suitable for high-rigidity high-pressure cylinders.
(2) It is a bolt with a tight joint surface. According to the tightness of the inspection joint surface of the feeler gauge, the value and the pressed-out trace are measured and the joint surface is repaired. This method can eliminate the influence of the cylinder arc on the clearance.
2. The use of appropriate cylinder seal materials The quality of turbine sealants for turbine cylinders is uneven. When selecting turbine sealants for cylinders, it is necessary to select a regular manufacturer with a reputation in the industry to guarantee the quality of the cylinders after maintenance. Sex.
3. Partial repair welding method Since the cylinder joint surface is steam washed or corroded groove marks, select the appropriate electrode to fill the groove marks flat, use a flat plate or flat feet to develop traces, study scraping bead and joint surface in the same plane. When the deformation of the cylinder joint surface is large or the steam leakage is serious, one or two 10-20 mm wide clearance gap seals are welded on the joint surface of the lower cylinder, and then measured with a flat rule or a button on the cylinder, and the red sand is applied for scraping. Until the gap is eliminated. The process for this operation is also very simple. The cylinder is preheated to 150°C before welding, and then subsection or back welding is performed at room temperature. Select austenitic electrodes, such as A407, A412, after welding with asbestos cloth covered insulation slow cooling. After cooling to room temperature, it is polished and scratched.
4. Cylinder joint surface coating or spray When the cylinder joint surface leakage of a large area, the gap is about 0.50mm, in order to reduce the amount of work scraping, coating process can be used. The cylinder is used as the anode, and the coating is used as the cathode. The electrolytic solution is repeatedly applied on the joint surface of the cylinder. The thickness of the coating is determined according to the size of the gap between the cylinders. The type of the coating should be based on the material of the cylinder and the scraping. Depending on the process. Spraying is to use a special high-temperature flame spray gun to heat the metal powder to a molten or plastic state and spray it on the treated cylinder surface to form a coating method with the desired properties. Its characteristic is that the equipment is simple, the operation is convenient and the coating is firm, and the temperature of the cylinder after spraying is only 70° C.-80° C. It will not cause deformation of the cylinder, and it can obtain heat-resistant, wear-resistant and corrosion-resistant coatings. Note that the cylinder surface must be polished, degreasing, and napped before coating and spraying, and the coating should be scratched after coating and spraying to ensure the tightness of the bonding surface.
5. Joint padding method If the partial gap leakage at the joint surface is not large, the 80-100 mesh copper mesh can be heat-treated to reduce the hardness, and then cut into an appropriate shape and spread on the steam leakage surface of the joint surface. Cylinder sealant. If the gap between the joints is large and the leakage is serious, 50mm deep and 5mm deep groove can be opened on the upper and lower joint surfaces. The toothed mat with IGr18Ni9Ti is set in the middle, and the thickness of the toothed mat is generally 0.05-0.08mm larger than the depth of the groove. The same shape stainless steel gasket can be used for adjustment.
6. Method of controlling bolt stress If the deformation of the cylinder joint surface is small and uniform, replace the bolt with a gap or increase the preload of the bolt. Press at the same time from the middle to both sides, that is, tighten the bolt from the largest point of the vertical arc or where the deformation of the force is the greatest. Theoretically speaking, the pre-tightening force of the control bolt can be calculated using the formula d/L ≤ A, but since the data and measurement means of this calculation are still being studied, it is determined empirically based on the maximum allowable stress of the bolt.
cylinder
The following is the calculation formula for the theoretical output of the cylinder:
F: cylinder theoretical output force (kgf)
F': output force at an efficiency of 85% (kgf)--(F'=F×85%)
D: cylinder bore (mm)
P: working pressure (kgf/cm2)
Example: What is the theoretical output force of a cylinder with a diameter of 340mm and a working pressure of 3kgf/cm2? What is the output force of the bud?
Connect P, D, find the points on F, F', get:
F=2800kgf; F'=2300kgf
The cylinder bore diameter is selected during engineering design and can be determined from the empirical table 1-1 according to the use pressure and theoretical thrust or pull force.
Example: The use pressure of a cylinder is 5kgf/cm2. When the cylinder is pushed out, the thrust is 132kgf (cylinder efficiency is 85%). Q: How large is the cylinder bore diameter?
â— From cylinder thrust 132kgf and cylinder efficiency 85%, the theoretical thrust of the cylinder can be calculated as F = F'/85% = 155 (kgf)
◠By using the pressure of 5kgf/cm2 and the theoretical thrust of the cylinder, it can be found that the cylinder with the bore diameter of 63 can meet the requirements.
VIII. Cause Analysis During the cylinder operation, cylinder leakage and cylinder deformation are the most common equipment problems. The tightness of the cylinder joint surface directly affects the safe and economic operation of the unit, and the combined surface of the cylinder is overhauled to make it tighter. It is an important task for the maintenance of the cylinder. In the process of dealing with the leakage of the combined surface, it is necessary to carefully analyze the cause of the formation. Depending on the degree of deformation and the size of the gap, various methods can be comprehensively applied to meet the strict requirements of the joint surface. The reason is as follows:
1. The cylinder is cast and the cylinder must be treated after aging. It is necessary to store some time to completely eliminate the internal stress generated by the cylinder during the casting process. If the aging time is short, then the processed cylinder will be deformed in the subsequent operation, which is why some cylinders will still have leakage steam in the subsequent operation after the first leakage treatment. Because the cylinder is still constantly deformed.
2. The force applied by the cylinder during operation is very complicated. In addition to the pressure difference between the gas inside and outside the cylinder and the static load of the weights of the various components contained therein, the reaction force to the static part when the steam flows out of the stationary blade is also taken. The forces acting on the cylinders in the cold and hot state of the connecting pipes, under the interaction of these forces, cause the plastic deformation of the cylinder to cause leakage.
3. The increase or decrease in the load of the cylinder is too fast, especially the rapid start-up, shutdown and change in the operating conditions when the temperature is large, the warm cylinder is not in the right way, and the insulation layer is opened prematurely during shutdown, etc. Large thermal stress and thermal deformation.
4. The cylinders produce stress during machining or after welding, but they are not eliminated by tempering the cylinders, resulting in large residual stresses in the cylinders and permanent deformation during operation.
5. In the process of installation or overhaul, the expansion gaps of the inner cylinder, the cylinder partition, the spacer sleeve and the steam jacket are not suitable due to the inspection process and the maintenance technology, or the expansion gap of the lug pressure plate is not suitable. Huge expansion force causes the cylinder to deform.
6. The cylinder sealant used is of poor quality, has too much impurities or is not of the correct type; if there are hard particles in the sealant of the cylinder, it will be difficult for the sealing surface to be tightly bonded. VIF900 high temperature cylinder sealant is the latest turbine cylinder seal material. High, medium and low pressure cylinders can be used universally to avoid cylinder leakage caused by improper model selection.
7. Insufficient tightness of cylinder bolts or defective material of bolts. The tightness of the cylinder joint surface is mainly achieved by the tightness of the bolt. The thermal stress and high temperature generated when starting and stopping the unit or increasing or decreasing the load will cause the stress relaxation of the bolt. If the stress is insufficient, the preload of the bolt will gradually decrease. If the bolts of the cylinder are not of good quality, the bolts will be stretched under the action of thermal stress and expansion force of the cylinder during a long period of operation, plastic deformation or fracture will occur, and the tightness will be insufficient, causing the cylinder to leak.
8. The cylinder bolts are not in the correct order. The general cylinder bolts are fastened from the middle to the sides simultaneously when they are fastened, that is, they are fastened from the largest place of the vertical arc or the place where the force is deformed the most. This will move the clearance where the deformation is greatest to the front and rear of the cylinder. End transfer, the last gap disappears. If it is from the two sides to the middle, the gap will be concentrated in the middle, the cylinder joint surface forms a bow gap, causing steam leakage.
Nine, the application of the cylinder printing (tension control), semiconductor (spot welding machine, chip grinding), automatic control, robots and so on.
CNC Lathe With Linear Guideway Slant Bed
Desktop Cnc Lathe,Cnc Turning Machine,Cnc Lathe Machine,Slant Bed Cnc Lathe
Ningbo junfa CNC Equipment Co. Ltd. , https://www.junfacnc.com
